About Me
Gustavo A. Cardona received his bachelor’s degree in Electrical Engineering from the Universidad Nacional de Colombia, in 2017. Currently, he is a Ph.D. student in Mechanical Engineering from Lehigh University with expected graduation in 2025. He belongs to the Explainable Robotics lab and SWARMS lab and Autonomous and Intelligent Robotics Laboratory AIRLab at Lehigh University. Under the supervision of professors Cristian Ioan Vasile and David Saldaña.
Research Interests
Aerial robotics, modular robots, and cooperative robotics.
Temporal logic, robot motion planning
Control, formal methods, and optimization.
Academic Timeline
- 2020-present
Ph.D.Mechanical Engineering at Lehigh University - 2011-2017
B.Sc. Electrical Engineering- Universidad Nacional de Colombia - May 2016 – Feb 2017
Research assistant student - Jul 2012 – Jan 2015
Engineering and innovation department manager
Publications
2021
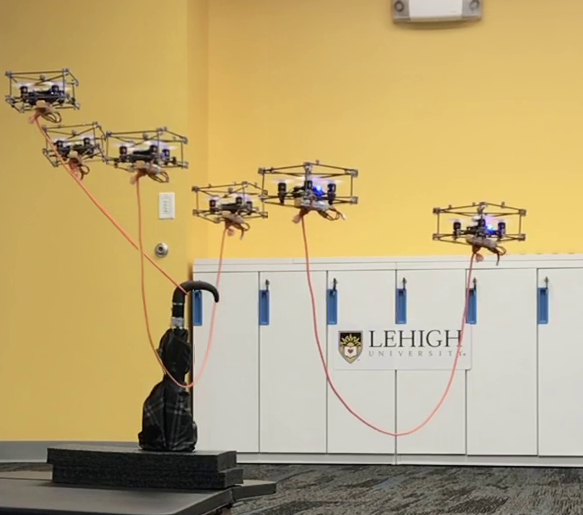
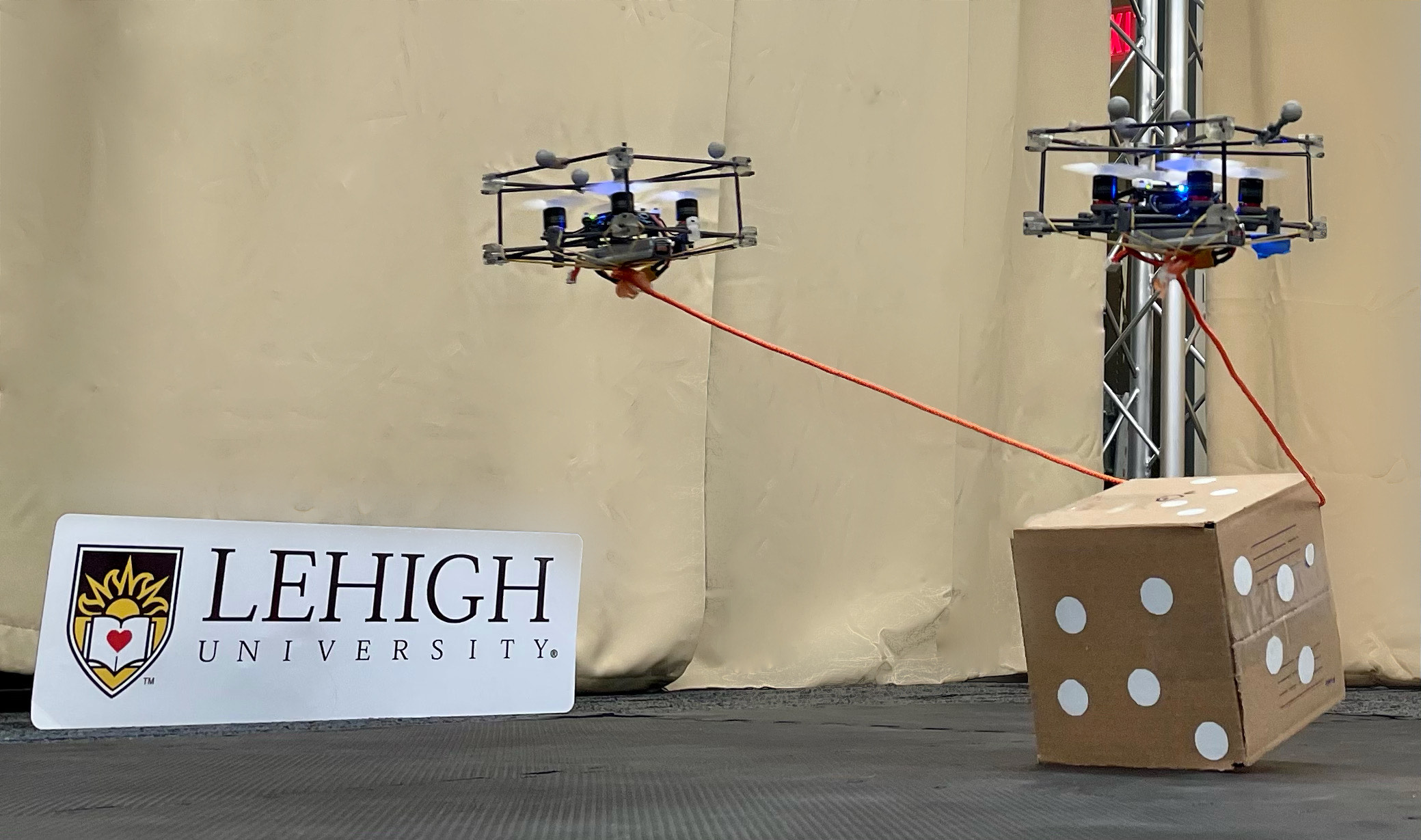
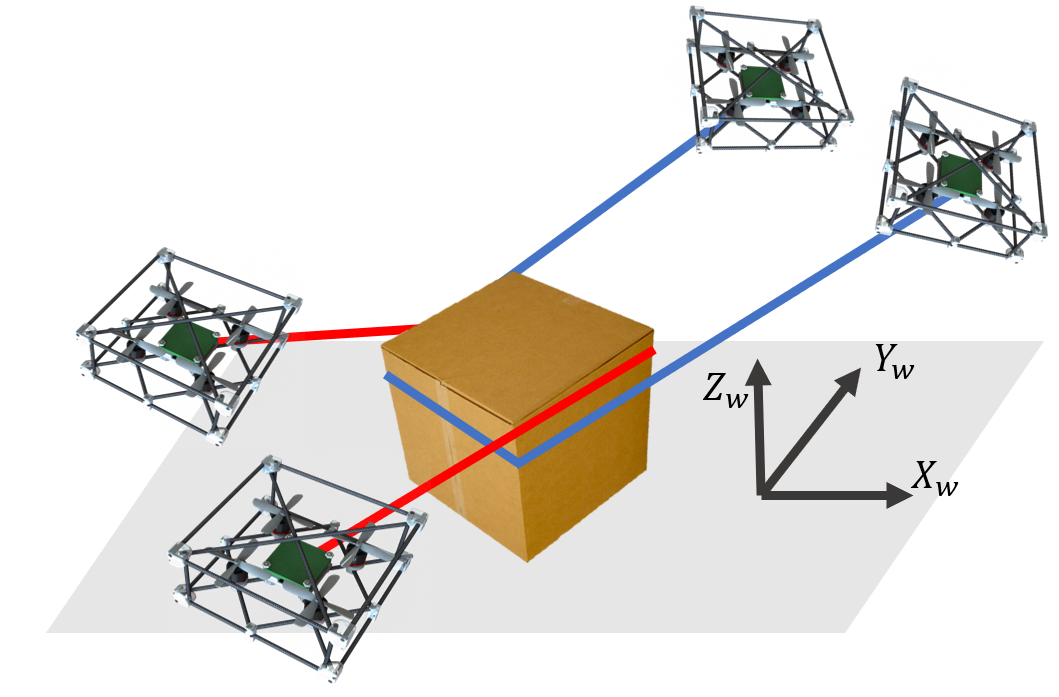
The Catenary Robot: Design and Control of a Cable Propelled by Two Quadrotors Journal Article
In: IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 3857-3863, 2021, ISSN: 2377-3766.